
Ladybugs and Asian beetles are not only charming to look at, but these little insects play vital roles in our ecosystems. In Northern California, their presence is more prominent than you might think. Whether you’re a nature enthusiast or just curious about these fascinating creatures, you’re in for some intriguing insights. Let’s explore some surprising facts about ladybugs and Asian beetles that you probably didn’t know!
1. Differences Between Ladybugs and Asian Beetles
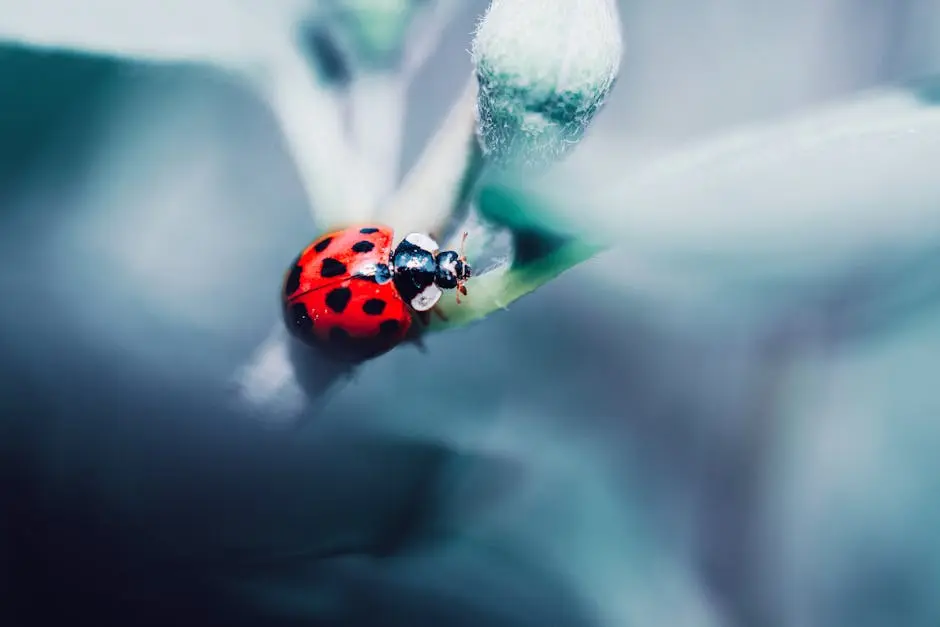
When we talk about ladybug vs Asian beetle, there are subtle yet significant differences that can help us distinguish between the two. While both are often mistaken for each other due to their round bodies and colorful appearance, they belong to different families. The ladybug, or ladybird beetle, is a member of the Coccinellidae family, while Asian beetles, often referred to as the multicolored Asian lady beetle, are part of the Harmonia axyridis species. One of the most notable differences lies in their coloration; ladybugs typically exhibit bright red or orange with black spots, whereas Asian beetles can show a range of colors, including yellow and black without spots.
Another clear distinction is their behavior and habitat preferences. Ladybugs tend to be solitary insects, often found in gardens and fields where they can readily access aphids, their favorite snack. On the other hand, Asian beetles are more social and have been known to gather in large numbers, especially during the fall months as they seek shelter. This gathering behavior often leads to people misidentifying them as a threatening pest when, in fact, they are also beneficial for controlling pest populations.
2. The Role of Ladybugs as Natural Pest Controllers
Ladybugs are celebrated as natural pest controllers and play a vital role in sustaining healthy garden ecosystems. They primarily feed on aphids, which can wreak havoc on plants if left unchecked. A single ladybug can consume hundreds of aphids in a week, making them a gardener’s best friend. By keeping aphid populations in check, ladybugs help promote the overall health of many garden plants. This pest control service is not just beneficial but essential for organic gardening, as it reduces the need for chemical pesticides that can harm other beneficial insects.
Interestingly, ladybugs are not picky eaters. While aphids are their main course, they also enjoy a diet of mites, scales, and even thrips. This diverse diet aids in pest control across various plants and landscapes. Furthermore, the presence of ladybugs can signal a balanced ecosystem, attracting other beneficial insects and creating a thriving garden environment. Their voracious appetite for destructive pests provides gardeners with a natural alternative to chemical interventions.
3. Asian Beetles: Unwelcome Guests or Helpful Allies?
Asian beetles have earned a mixed reputation as they are often perceived as unwelcome guests in our homes. Initially introduced to North America for their pest-controlling capabilities, these insects are similar to ladybugs in their diet and behavior. While they too help manage aphid populations, their tendency to invade homes during the cooler months can lead to frustration for homeowners. Unlike ladybugs, Asian beetles can emit a foul odor when disturbed and leave behind yellowish stains, which adds to their pesky reputation.
However, it’s important to consider their ecological contributions. Just as ladybugs do, Asian beetles play a role in controlling aphids and other pests that can damage crops. They thrive in gardens and agricultural landscapes, promoting healthy plant growth by keeping pest populations in check. While they may sometimes invade our space, understanding their beneficial role helps us appreciate these little creatures more and find ways to coexist harmoniously.
4. Life Cycle Insights: From Egg to Adult
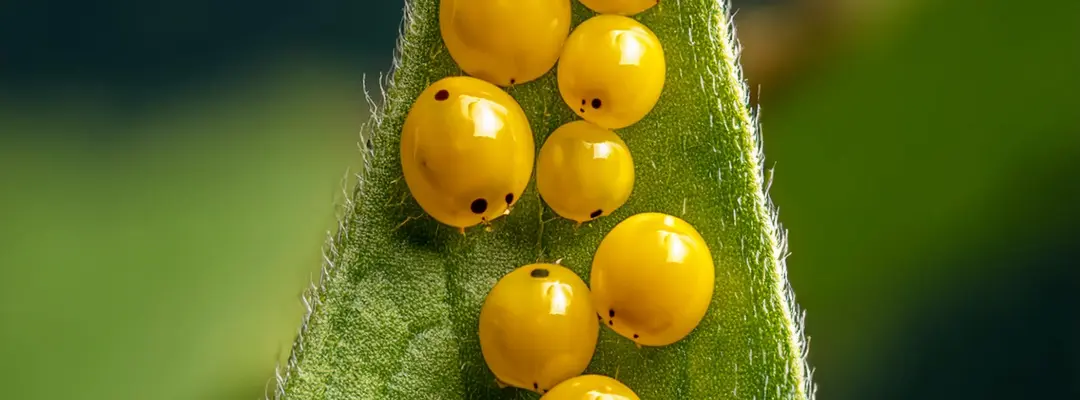
The life cycle of both ladybugs and Asian beetles is a fascinating journey that begins with eggs. Female ladybugs can lay hundreds of eggs at a time, often on the underside of leaves where food sources like aphids are plentiful. After about a week, the eggs hatch into larvae, which are voracious eaters themselves. These larvae may not look like the adult beetles with their bright colors; instead, they are dark, spiny, and somewhat intimidating in appearance. However, it’s this youthful stage that plays a crucial role in pest control.
As the larvae undergo several molts, they grow and become more efficient predators. After about two to three weeks, they pupate, eventually transforming into adult beetles. This remarkable metamorphosis draws parallels to butterflies, showcasing the incredible changes within these small creatures. Adult ladybugs can live up to a year, and during this time, they continue to contribute to pest management in gardens. Understanding this life cycle not only highlights the importance of ladybugs and Asian beetles but also emphasizes their role in sustaining our ecosystems.
5. The Colorful Varieties of Ladybugs
When it comes to ladybugs, the vibrant colors and patterns can often captivate our attention. While most people immediately recognize the classic red ladybug with black spots, several remarkable varieties inhabit Northern California. Some species feature bright orange shells, while others may appear in shades of yellow or even with unique patterns of stripes or spots. The diversity in their coloration serves not only as an artistic display but also plays a role in their survival. Different colors can help them blend into their environments, providing camouflage from predators.
Interestingly, color variations can also be indicative of their geographical location and habitat adaptations. For instance, some ladybugs residing in drier areas may develop different pigmentation compared to those in wetter environments. This adaptability ensures their survival across diverse ecosystems. Understanding the world of ladybug varieties not only adds to our appreciation of these charming insects but also highlights the significance of biodiversity in maintaining a resilient environment.
6. Asian Beetle Adaptations to Northern California’s Climate
Asian beetles have demonstrated remarkable adaptations that enable them to thrive in Northern California’s unique climate. Originally from East Asia, these beetles have successfully adjusted to a variety of environmental conditions, showcasing their resilience and versatility. They can tolerate cool temperatures, which is part of why they seek shelter in homes during the autumn. This behavioral adaptation allows them to survive the winter months, ensuring their return when temperatures warm up again.
Moreover, Asian beetles are capable of modifying their diet based on the availability of food sources in different climates. During the warm season, they feast on aphids and other pests, but as conditions fluctuate, they can shift their dietary preferences. This flexibility not only supports their survival but allows them to remain, effective pest controllers, even when faced with environmental challenges. By studying these adaptations, we gain insight into how these insects have managed to establish themselves in diverse ecosystems across Northern California.
7. The Importance of Biodiversity in Gardens
Biodiversity is a cornerstone of healthy gardens and ecosystems, and the presence of ladybugs and Asian beetles plays a significant role in supporting this variability. A diverse garden invites various insect species that contribute to pollination, pest control, and overall plant health. When different species coexist, each brings its unique abilities to the ecosystem, creating a balance that benefits all. For instance, the presence of ladybugs helps manage pest populations, while other species can enhance soil health and promote plant growth.
Encouraging biodiversity can also attract beneficial insects, increasing the chance that natural pest control will occur. An abundance of flowering plants can lure in ladybugs and other predatory insects, establishing a thriving insect community. This interconnectedness showcases the importance of maintaining a diverse range of species, where even the smallest insect contributes to the elegance of the ecosystem. By nurturing biodiversity in gardens, we create resilient environments that sustain both plant and insect life.
8. How to Identify Common Species
Identifying common species of ladybugs and Asian beetles can be an engaging and educational experience for nature enthusiasts. To differentiate between species, start by observing the color and markings on the beetles’ shells. For instance, the classic seven-spotted ladybug is identifiable by its round shape and the distinct seven black spots on its red exterior. Alternatively, look for the Asian beetle, which may exhibit no spots or an array of colors. This variation can make it intriguing yet challenging to distinguish them at times.
Another useful identification method involves paying attention to their behavior. Ladybugs are generally solitary, whereas Asian beetles tend to gather in larger numbers, especially in homes during late autumn. Additionally, observing their feeding habits can provide clues; ladybugs will primarily be seen on plants as they devour pests, while Asian beetles may be spotted in more diverse settings. By learning the distinguishing features and behaviors of these beneficial insects, you can become a more informed and aware observer of the natural world.
9. Conservation Efforts for Our Essential Insects
Conservation efforts for ladybugs and Asian beetles are crucial in maintaining the delicate balance of ecosystems, particularly in agricultural areas. Pesticides, habitat loss, and climate change pose significant threats to these essential insects. To counteract these issues, many communities are implementing eco-friendly practices that protect beneficial insect populations. For instance, promoting organic gardening methods, planting native flora, and reducing pesticide usage are all steps that contribute to healthier ecosystems and the preservation of these vital species.
In addition to grassroots efforts, researchers and entomologists are studying the behaviors and population dynamics of ladybugs and Asian beetles. By understanding their life cycles, habitat preferences, and ecological roles, scientists can develop targeted conservation strategies. Implementing educational programs that inform the public about the importance of these insects also supports conservation initiatives. As we strive to protect and conserve our natural world, recognizing the invaluable contributions of ladybugs and Asian beetles will help foster a deeper appreciation for these small yet mighty creatures.




